Laryngeal surgery in Iran
The larynx is an important organ in the body. It plays a high role in aspiration, speaking and protecting the trachea and lungs. However, it is exposed to too many diseases and tumors (cancer and benign tumors) that needs surgery. The laryngeal cancer surgery includes the partial or total removal of the larynx and many other partial procedures within the larynx. These operations are complicated ones, it needs highly qualified surgeons and highly equipped hospitals, which may be not facilitated in your country or it costs a large sum of money. Iran offers you a good chance for your surgery in excellent hospitals and distinct ENT and neck surgeons like Dr. Masoumeh Saaedi at affordable costs. Please continue reading to know more on laryngeal surgery in Iran with Dr. Saeedi.
What is larynx?
At the end of the oral pharynx, it is divided into the trachea and the esophagus. The upper part of the respiration apparatus, which contains the epiglottis, the extent of the pharynx (hepopharyngeal), vocal cords and connects in the lower to the trachea, is called the larynx or voice box, and appears in the anterior part of the neck. It involves the act of respiration, protection of the trachea and lungs, and sound production.
What are the causes to undergo laryngeal surgery?
Larynx is exposed to many factors (bacterial, viral, environmental, traumatic and many others) that may cause tumors (benign or malignant) that arise within the larynx or in the surrounding tissues (basically, laryngeal carcinoma) and/or as metastasis, that affects the larynx and their functions.
In most cases, the surgery will be the main option for treating the tumors.
As well, many other lesions affect the larynx and summon surgery, such as:
- Spasmodic dysphonia that needs laryngeal denervation or reinnervation surgery that may be a good option for achieving a long-term symptoms control in contrast to botulinum toxin injection that gives good results for a short-term.
- Laryngeal granuloma surgery combined with proton pump inhibitors may lessen granuloma returning from 50% to 38%, while laser CO2 surgery is the best option for the treatment of laryngeal haemangioma (benign vascular tumor).
- Laryngeal framework surgery (vocal cord paralysis, laryngeal stenosis, cases of cancers, nerve damage surgery, and trauma to the larynx)
On the other hand, laryngeal cartilage fractures should be amended with mini plates to regain its normal position.
Another cause for an operation is laryngeal web, in which the larynx is covered with a web-like tissue that restricts air passing in and out the windpipe (larynogofissure).
Neck surgery such as thyroid surgery may cause laryngeal nerve damage as in the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve and/or the inferior laryngeal nerve.
Sometimes, open-heart surgery may cause recurrent laryngeal nerve injury. Every case of these problems needs a special laryngeal nerve surgery.
Larynx disorder symptoms
The symptoms of larynx disorders may vary widely due to the numerous functions of the larynx, its structure, the nature of some tumors, their site, and the patient physic. However, the most common symptoms are:
- Dysphonia/aphonia
- Dysphagia
- Dyspnea
- Aspiration problems
- Blood-tinged sputum
- Fatigue and weakness
- Cachexia
- Pain
- Halitosis
- Expectoration of tissue
- Neck mass
- Otalgia, where ear pain may be a result of laryngeal cancer in some cases.
What is laryngeal surgery?
Usually, surgery is performed to treat many kinds of laryngeal and hypopharyngeal benign and malignant tumors, and other special cases. The surgeon removes the tumor and some of the surrounding tissues to prevent its recurrent. Surgery may be the only treatment for some kinds of tumors.
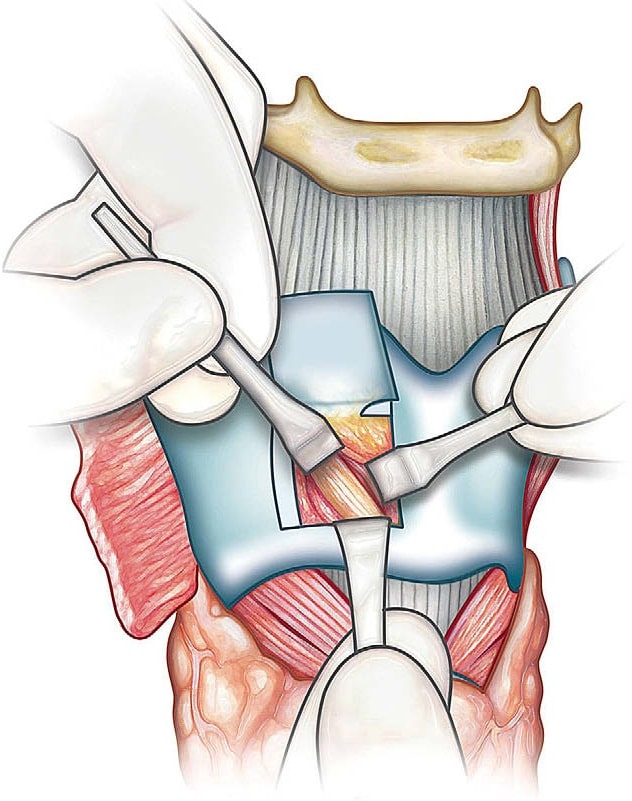
In total laryngectomy surgery, the ENT surgeon removes the entire larynx aiming to take off the tumor and restore the lost functions through the reconstructive surgery. This surgery may include the shift of the airway to the neck through an opening called a stoma.
In partial laryngeal surgery, the surgeon removes the tumor and a little of surrounding tissues and restore the most of larynx (near-total laryngectomy). Laryngeal cancer treatment after surgery in both cases may include chemotherapy and radiation.
The surgeon may use traditional instruments like scalpels and scissors and/or the new techniques such as endoscopic, laser surgery and micro surgery.
Why opt for laryngeal surgery in Iran?
Laryngeal surgery is an acute surgery that requires high experiences and advanced techniques. As mentioned above, Iran has well-equipped hospitals, and highly trained ENT surgeons like Dr. Saaedi besides the low cost due to economic factors such as their cheap currency.
These factors make Iran a good place to undergo your surgery in. Not to mention that you can enjoy their cultural and historical items and their marvelous nature.
Why undergo laryngeal surgery in Iran with Dr. Saeedi?
Among ENT doctors in Iran, Dr. Masoumeh Saeedi stands out due to her scientific excellence, high practical experience, and her humane conduct with her patients. Dr. Saeedi is a board specialized in ENT (ear, nose and throat) and head and neck surgery, and she was able to become a professor at the university when she was only 33 years old.
Dr. Saeedi now has more than 15 years of experience, during which she has performed more than 5,000 successful surgeries, including many laryngeal surgeries, for Iranian and foreign patients.
Dr. Saeedi benefits from teaching at the Baqiatallah University of Medical Sciences in Tehran and supervising medical students there to stay in touch with new scientific research. Furthermore, she always enhances her professional expertise on the latest technologies in the world by following many specialized courses in countries such as France, Germany, Portugal, South Korea, Malaysia and others.
If you decide to have a laryngeal surgery in Iran with Dr. Saeedi, you can guarantee that you are in safe hands and that you will receive the best possible treatment for your condition while having online follow-up even after you leave Iran. You can communicate now on this site or via the social media of the doctor so that you can get a free online consultation about laryngeal surgery in Iran with Dr. Saeedi.
Cost of laryngeal surgery in Iran with Dr. Saeedi
The average cost for laryngectomy reach $17,000 in some countries, which is a large sum perhaps you are not able to pay it. Iran offers you a good chance to do your surgery in the best hospitals at the hands of Dr. Saeedi who is one of the cleverest surgeons for as low a a quarter this sum. Please contact us now to have a free online consultation and price quote on laryngeal surgery in Iran with Dr. Saeedi.
Who is to undergo laryngeal surgery?
People with the following conditions are candidates to undergo laryngeal surgery:
- Benign tumors in polyps, nodules, and cysts that may especially affect vocal professionals like singers, teachers, public speakers…etc.
- Malignant tumors within the larynx and their surrounding tissues.
- Many diseases that do not respond to medical conservative treatment may need laser or other kinds of surgery like cricopharyngeal achalasia, subglottic stenosis, spasmodic dysphonia, laryngeal web, and laryngeal cleft.
- Some other surgery on or near the neck, thyroid or parathyroid glands, and chest may cause injury to the nerves that lead to the voice box (laryngeal paralysis after surgery).
Preparation for surgery
Your doctor must explain the surgery, risks and expectations. You need to do some other thing in preparation for laryngeal surgery:
- Stop eating and drinking after the midnight preceding the day of surgery
- Stop blood thinner medicine before a week of surgery
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol and other medicine according to your doctor’s advice.
You may need some blood tests, CT scan, and some other consultations and images.
Laryngeal surgery: How is it done?
Laryngeal surgery aims to eradicate the tumor and some of the first margins and restore larynx functions by reconstructive surgery. It may be done by general anesthetic or local anesthetic according to the extent of surgery.
The surgery may involve partial or total removal of the larynx (Laryngectomy).
In the total removal surgery, the surgeon makes an incision in the skin of the upper part of the front side of the neck under the mandibular bone and another vertical incision in the middle of the neck a little down to the upper part of the trachea. This position enables the doctor to eradicate the entire affected larynx and put a tube in the trachea (tracheostomy) for transferring the airway to the neck.
The patient can no longer speak normally, while he could swallow food and liquid normally after ten days. He/she has to learn other methods of speaking.
Another kind of relatively extensive surgery is a three-quarter (near-total or Pearson) laryngectomy that retains swallowing and phonating mechanism but the patient need a tracheostomy for the rest of his life to protect breathing.
In other cases, the surgeon may remove the front soft part of the larynx and the following thyroid cartilage (hemilaryngectomy). However, the surgery may be more invasive in vertical partial laryngectony.
Partial removal surgery aims to take out all of the cancer and some of the surrounding tissue but to retain as much as possible of larynx tissues. Alike, in supraglottic cancer, the surgeon removes a part of the larynx above the vocal cords.
There are many types and techniques of laryngeal surgery. The surgeon may choose the appropriate methods and techniques for laryngeal surgery according to every case.
In endoscopic surgery or laryngeal microscopic surgery, the surgeon inserts through the oral cavity a thin tube with a light and camera on the end of it. This way the surgeon could see well the tumor and make a biopsy. The surgeon may also insert a surgical instrument through the endoscope to remove the tumor on the vocal cords or other early stages of larynx tumors.
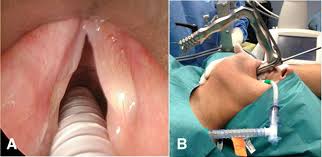
The surgeon can also use laryngeal laser surgery by the endoscopic technique, by which, he/she could vaporize or cut out the tumor. However, the laser may cause a hoarse voice if it used to eradicate a part of a vocal cord and does not leave any remnant to be examined. This method is excellent for the treatment of early/intermediate glottis and supraglottic cancer), open supraglottic partial laryngectomy and supracricoid partial laryngectomy.
While laryngeal amyloidosis excision surgery by endoscopic CO2 laser gives an excellent outcome in cases of extent amyloidodosis tumor and the surgeon may perform microscopic laryngeal surgery under local anesthesia, laryngeal papilloma can be similarly ablated by CO2 laser. Office-based laryngeal laser surgery and microlaryngeal surgery are increasingly becoming more widespread day after day.
Recently, in transoral robotic surgery, the surgeon controls the arms of the robot and obtain a better vision and the possibility of manipulating the tissues by the retractors. This laryngeal robotic surgery has a large benefit for adult benign laryngeal masses.
In cordectomy surgery, the surgeon may excise all or part of the vocal cord. This kind of treatment is employed for superficial glottis (vocal cord) cancers. In the case of extent surgery and removing all vocal cords, the speech is no longer possible, while in one-side vocal cord paralysis or immobility, recurrent laryngeal reinnervation surgery is a good option to deal with the hoarseness.
Another common procedure is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux surgery, in which the surgeon expands the lower sphincter. The operation blocks acid from going up to the esophagus, while laryngotracheal reconstructive surgery involves implanting a small piece of cartilages into the narrowed part of the trachea to widen it.
While Laryngeal cleft surgery is rare, but laryngeal cyst surgery forms about 4.9% of laryngeal surgery and can be done through laryngeal endoscopic surgery.
In patients who suffer from severe chronic aspiration, laryngeal diversion surgery is a more active operation for lessening pollution on the pulmonary tract.
High-Frequency Jet Ventilation can be used as an alternative ventilatory approach in anesthesia and intensive care medicine. Otherwise, it can be used during the diagnostic or surgical procedures for patients who suffer from airway disease and to support gas exchange in cases of severe pulmonary failure.
Meanwhile, laryngeal mask airway in laparoscopic surgery is a great addition to the safety of anesthesia.
Laryngeal surgery recovery time: What to expect?
In total laryngectomy, the patient remains in the hospital under supervision for several days. He/she may have a tracheostomy and a feeding tube and drainage. The patient will not be able to speak, breathe and swallow, and smelling will somehow change. The speech specialist will teach you how to speak according to your new implant, (the electrolarynx, or esophageal speech, or tracheoesophageal speech through a tracheoesophageal puncture (TEP) with a voice prosthesis.). The surgery needs 1-2weeks for recovery.
Partial laryngeal cancer surgery may differ between near-total laryngectomy and laser endoscopic surgery. The first needs attentive care and contains a tracheostomy and a feeding tube and drainage, but the second is an outpatient surgery and the patient is discharged to go home after surgery being able to speak, breathe, and swallow well.
Pros and cons of laryngeal surgery
The survival rate after five years of total laryngectomy surgery is about 90% from all cases, while most other partial surgeries are so far safe, maintain, and restore the function of the larynx. There are some risks and complications, but the benefits overpass their disadvantages, and a highly experienced surgeon like Dr Saeedi will reduce the negative results to a large degree.
Benefits of laryngeal surgery
The result of the surgery depends on the stage of the tumor. The survival rate (five years) may reach over 90% in the early stage of tumors, while the survival rate decrease in stages 3 and 4, and the patient may need radiation and chemotherapy.
This is while the survival rate for five years is about 53.7% for patients with subglottic squamous cell carcinoma.
In most procedures, the patient restores the function of speech, breathe, swallow, and smell. These outcomes are worthy and reliable, not to mention saving the life itself.
Laryngeal surgery risk and complication
Total laryngectomy complications may include:
- Hematoma formation: after the first 24 hours, it can be prevented by suitable hemostasis and by a drain.
- Fistula formation: it happens in up to 30% of cases that small fistulas recover itself, but large fistula needs coverage by pectoralis flap.
Other complications include post operation hypocalcemia, Chyle leak, stomal strictures, carotid rupture and nerve injury. However, most of these laryngeal cancer surgery side effects are temporary and can be prevented by an experienced surgeon.
Generally speaking, partial surgery is safe, but there are many complications after surgery. Those complications differ according to the surgery and anesthesia (general or local), such as bleeding or infection, but, for instance, in phono surgery (surgical operations related to human voice), scarring will alter the character of the voice. In addition to these risks, there are some unique complications due to the surgery or radiation and chemotherapy like:
- Loss of upper body strength after laryngectomy
- Psychosocial trauma from surgery and/or radiation therapy
- Limited mobility of the neck
- Daily stoma care
- Vocal cord–powered voice loss in some procedures
- Aspiration pneumonia in some procedures
- Radiation-induced neoplasms of the neck
- Dysphagia
- Pharyngeo-cutaneous fistula
- Osteoradionecrosis
- Chondroradionecrosis
- Chronic pain
- Breathing difficulties
- Stoma infections
- Laryngeal paralysis after surgery
Another complication as a result of recurrent laryngeal intubation is laryngeal edema.
Generally speaking, laryngeal surgeries are interesting essentially in the safety of the patients and in maintaining their larynx functions. Therefore, patients should endure some risks for achieving their final goals. An experienced surgeon like Dr. Saeedi may reduce and diminish risks and complications by using the latest techniques such as laser and microscopy surgery.
Frequently asked question about laryngeal surgery
Is laryngeal surgery dangerous?
Danger relates to the reason for surgery. In benign tumor and first and second stages of cancer, the surgery is safe and the survival rate is about 90%, but in the third and fourth stages, the survival rate is lower and the patient may need radiation and chemotherapy.
Is laryngeal surgery outpatient?
This depends on the surgery itself. The patient needs to stay in the intensive care for 1-2 days in some kinds of surgery, such as total larynx removal, near-total laryngectomy, and in hemilaryngectomy or vertical partial laryngeectomy surgery. This is while most of the other surgeries are outpatient.
What to do after laryngeal surgery
If you have undergone a large surgery (total larynx removal or near-total removal), you need to stay one or two days in an intensive care. You will eat and drink with a feeding tube until your throat recovers, which may take at least 1-2 weeks.

