Ear Discharge: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
Ear discharge is a common ear condition that may occur due to various factors such as ear infections, excessive earwax buildup, or certain skin disorders. This condition is typically characterized by yellow, white, green, or black fluid draining from the ear, medically referred to as otorrhea. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, causes, treatment options, and prevention strategies related to ear discharge.
![]() Causes of Ear Discharge
Causes of Ear Discharge
Ear discharge can result from several underlying conditions, including:
-
Ear Infections
External ear infection (otitis externa), often caused by bacteria or fungi.
Middle ear infection (otitis media), particularly common in children, which may lead to pus drainage from the ear. -
Earwax Buildup
Excessive accumulation of earwax (cerumen) can block the ear canal, causing irritation and sometimes leading to discharge.
-
Eardrum Perforation
In severe infections, the eardrum may rupture, allowing pus-like discharge to drain from the ear.
-
Water or Contaminated Substances Entering the Ear
Water entering the ear during swimming or bathing may promote bacterial or fungal growth, resulting in ear discharge.
-
Skin Conditions and Allergies
Certain dermatological conditions such as eczema or severe allergic reactions may cause increased ear secretions and subsequent discharge.
Symptoms of Ear Discharge
Ear discharge is often accompanied by several symptoms, including:
- Ear drainage that may appear yellow, white, green, or black and may have an unpleasant odor
- Ear pain, ranging from mild to severe, often worsening with touch or movement
- Temporary hearing loss due to blockage of the ear canal
- Itching or inflammation inside the ear
- Dizziness and balance disturbances in some cases
- Fever and chills, particularly when the cause is a bacterial infection
Ear Discharge in Children and Infants
Ear Discharge in Children
In children, ear discharge is most commonly caused by middle ear infections (otitis media). Symptoms may include pus-like drainage from the ear, reduced hearing, ear pain, and fever. This condition is more common in children under the age of five and should be treated promptly to prevent complications.
Ear Discharge in Infants
In infants, especially when a middle ear infection is present, purulent discharge may be observed. If a baby frequently pulls at their ear or develops a fever, it may indicate an ear infection with discharge. In such cases, medical evaluation is essential.
![]() Black Ear Discharge
Black Ear Discharge
Black ear discharge is often associated with a fungal infection, where fungi grow inside the ear canal. This type of infection is more likely to develop in warm and humid environments. The dark discharge may also be accompanied by an unpleasant odor. Proper treatment with antifungal ear drops or prescribed medications is necessary to resolve the condition.
Medical Treatment for Ear Discharge
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the infection. Whether the discharge results from bacterial infection, fungal growth, inflammation, or rarely viral causes, physicians prescribe targeted therapy accordingly.
1. Antibiotics
If the discharge is caused by a bacterial infection, oral or topical antibiotics may be prescribed. These medications eliminate the bacteria responsible for the infection and reduce inflammation. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include:
- Ampicillin
- Cephalosporins
- Mupirocin (for superficial infections)
2. Antifungal Ear Drops
When the cause is fungal, antifungal ear drops are recommended. These medications are specifically formulated to eliminate fungi and prevent their growth. Examples include:
- Natamycin
- Clotrimazole
- Ketoconazole
These are typically used for fungal infections of the external ear and help reduce discharge and relieve symptoms.
3. Pain Relievers and Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
To manage pain and inflammation, doctors may recommend medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. In more severe infections, stronger anti-inflammatory treatments may be considered.
4. Ear Irrigation or Suction
In some cases, professional ear cleaning, irrigation, or suction may be performed to remove accumulated discharge. This helps medications work more effectively and accelerates recovery.
5. Antiviral Medications (Rare Cases)
If the infection is viral in origin (such as herpes-related infections), antiviral medications like acyclovir may be prescribed.
6. Complementary Treatments
In certain situations, doctors may suggest natural oils such as tea tree oil or olive oil to soften earwax or soothe irritation. These are typically used as complementary treatments alongside primary medical therapy.
Important Considerations in the Medical Treatment of Ear Discharge
Medical treatment for ear discharge should always be supervised by a healthcare professional to ensure both safety and effectiveness. Using over-the-counter medications indiscriminately or self-prescribing antibiotics and ear drops may lead to antibiotic resistance and potentially serious complications.
If symptoms fail to improve after starting treatment—or if they worsen—prompt medical evaluation is necessary to reassess the condition and adjust therapy if needed.
To reduce the risk of recurrent ear infections, maintain proper ear hygiene and avoid exposing the ear to contaminated water, particularly during swimming or bathing.
![]() Home Treatment for Ear Discharge
Home Treatment for Ear Discharge
Home remedies can help reduce the symptoms of ear discharge, but it is important to note that these methods do not replace medical treatment. If symptoms worsen or do not improve, seeing a doctor is necessary. Some home remedies are simple and natural methods that can help relieve pain and reduce ear discharge.
If ear discharge is caused by a mild infection or wax buildup, some home remedies may help reduce symptoms. However, home remedies cannot replace medical treatment, and if symptoms worsen or persist, it is best to consult a doctor. Here are some effective home treatments for reducing ear discharge:
1. Using Olive Oil
Olive oil is one of the simplest and most effective home treatments for ear discharge. It helps soften earwax and can facilitate the removal of discharge. To use:
-
Put a few drops of warmed (not hot) olive oil into the ear.
-
Tilt your head to one side for a few minutes to allow the oil to enter the ear canal.
-
Dry the ear completely and wipe away any discharge with a soft cloth. This method can help relieve pain and soften earwax.
2. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar has antibacterial and antifungal properties and can help reduce infections and ear discharge. To use:
-
Mix one-quarter cup of apple cider vinegar with three-quarters cup of warm water.
-
Place a few drops of this solution in the ear.
-
Let it sit for a few minutes, then tilt your head to the other side to let the liquid drain. This method can help reduce discharge and prevent ear infections.
3. Using Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is another popular home remedy with antibacterial and antifungal properties. To use:
-
Dilute a few drops of tea tree oil with a carrier oil such as coconut oil or olive oil.
-
Apply this mixture around the ear using a clean cotton swab, avoiding putting it inside the ear. Tea tree oil can help reduce inflammation and infection.
Warm Compress
Using a warm compress can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation caused by ear pus. To do this:
-
Soak a clean cloth in warm water and place it on the affected ear.
-
Keep it there for 10–15 minutes to help reduce pain and inflammation. A warm compress can provide more comfort and help soften ear discharge.
Using Almond Oil
Almond oil is another natural method that can help soften earwax and reduce discharge. To use it:
-
Put a few drops of almond oil into the ear.
-
Then tilt your head to the other side so the oil fully enters the ear and softens the wax and pus.
Boiling Salt Water
Salt water is a simple and effective way to clean the ear and can help reduce pus and inflammation. To do this:
-
Dissolve a teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water.
-
Using a dropper, place a few drops of the salt solution into the ear.
-
Then tilt your head to the other side so the solution comes out along with the pus.
Important Precautions for Home Treatment of Ear Discharge
- Avoid hot or irritating substances: Oils or solutions should be warm—not hot—to prevent damage or irritation to the ear canal.
- Gentle and proper cleaning: If discharge is related to wax buildup, safe cleaning methods should be used carefully to avoid injuring the eardrum.
- Seek medical care if symptoms persist: If pain, swelling, or discharge worsens or fails to improve, professional medical evaluation is necessary, as home remedies may not be sufficient for serious infections.
Natural remedies such as olive oil, diluted apple cider vinegar, or tea tree oil may help relieve inflammation, but accurate diagnosis and effective treatment require consultation with a healthcare professional.
![]() Preventing Ear Discharge
Preventing Ear Discharge
1. Maintain Proper Ear Hygiene
- Avoid inserting cotton swabs into the ear canal.
- Dry ears thoroughly after swimming or bathing to prevent moisture buildup.
2. Use Personal Devices Only
- Do not share headphones, hearing aids, or other ear-related devices.
3. Treat Infections Promptly
- Manage respiratory or sinus infections early to prevent spread to the ear.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Medical attention is necessary if you experience:
- Foul-smelling pus discharge.
- Severe ear pain not relieved by painkillers.
- Temporary or permanent hearing loss.
- High fever, dizziness, or intense headache.
Conclusion
Ear discharge may indicate bacterial or fungal infections or other underlying ear conditions. Timely and appropriate treatment helps prevent complications. If symptoms appear or worsen, consult a physician for accurate diagnosis and proper care.
Online Consultation, Directly with Dr. Saeedi
Ask your question via WhatsApp, and if you wish, Send your photo for a more accurate assessment.
Free Consultation on WhatsApp

 Causes of Ear Discharge
Causes of Ear Discharge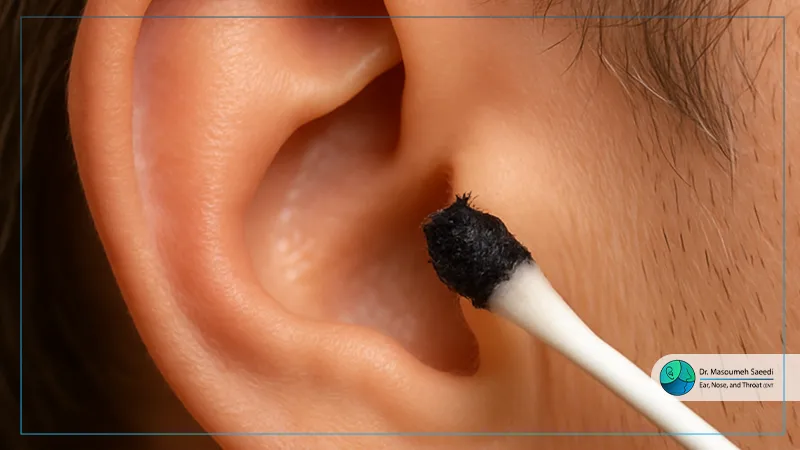 Black Ear Discharge
Black Ear Discharge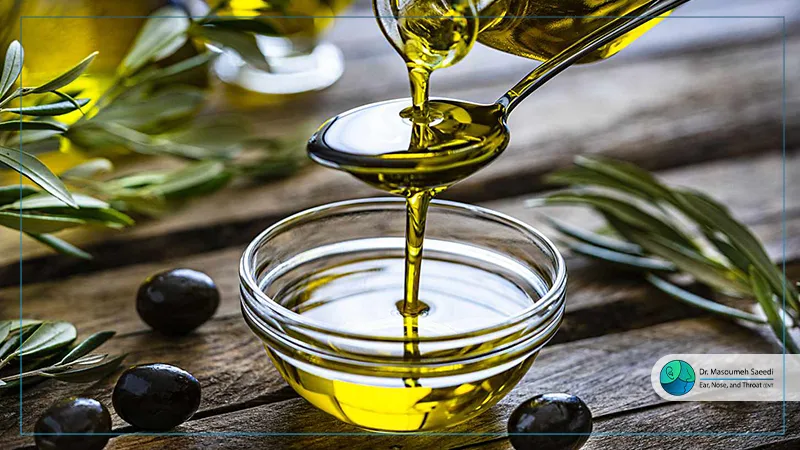 Home Treatment for Ear Discharge
Home Treatment for Ear Discharge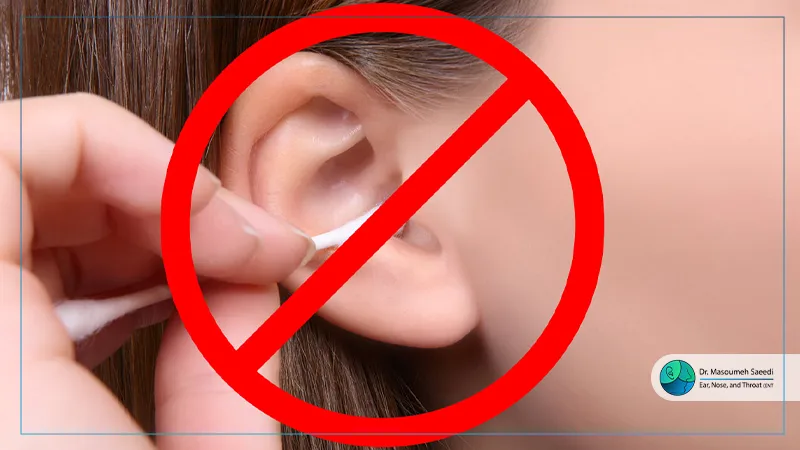 Preventing Ear Discharge
Preventing Ear Discharge