Betamethasone Ear Drops for Tinnitus: Uses, Side Effects, and Key Tips
Tinnitus, that persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears, can be a frustrating condition for many. It’s often caused by factors like ear infections, loud noise exposure, or even stress. Betamethasone ear drops, a corticosteroid medication, are designed to reduce inflammation in the ear canal, which can sometimes contribute to tinnitus symptoms. While not a direct cure, these drops can ease discomfort in cases where inflammation is a factor, such as in otitis externa. This guide dives into how betamethasone works, its benefits, and how to use it safely to manage tinnitus effectively.

Common Causes of Tinnitus
Tinnitus can arise from various sources, including ear infections, wax buildup, or damage from loud sounds. Inflammation in the ear canal, often linked to conditions like swimmer’s ear, can worsen the perception of ringing. Other causes include stress, certain medications, or even jaw issues. Identifying the root cause is essential for choosing the right treatment, as betamethasone is only effective for inflammation-related tinnitus.
How Betamethasone Ear Drops Function
Betamethasone is a powerful anti-inflammatory drug that targets swelling and irritation in the ear canal. By calming inflamed tissues, it can reduce pressure or discomfort that amplifies tinnitus sounds. The drops deliver the medication directly to the affected area, minimizing systemic side effects. For patients with otitis externa or allergic reactions in the ear, betamethasone can provide noticeable relief within days, though it’s not a solution for all tinnitus cases.
Mechanism Behind Corticosteroids
Betamethasone works by mimicking cortisol, a hormone that regulates inflammation. It blocks the release of chemicals that cause swelling, soothing the ear canal. This can indirectly lessen tinnitus severity if inflammation is a contributing factor. The localized action ensures quick results with minimal impact on the rest of the body, but it requires precise application to be effective.
Specific Uses for Tinnitus
Betamethasone is primarily prescribed for otitis externa, where inflammation may trigger or worsen tinnitus. It’s also used for allergic reactions or minor ear trauma that causes swelling. However, if tinnitus stems from neurological issues, vascular problems, or Meniere’s disease, betamethasone is unlikely to help. An ENT specialist can determine if these drops are suitable for your condition.
Safe Application of Betamethasone Drops
 Using betamethasone ear drops correctly is crucial for safety and effectiveness. Incorrect use can lead to contamination or reduced efficacy. Always follow your doctor’s instructions and maintain strict hygiene during application to avoid complications.
Using betamethasone ear drops correctly is crucial for safety and effectiveness. Incorrect use can lead to contamination or reduced efficacy. Always follow your doctor’s instructions and maintain strict hygiene during application to avoid complications.
Step-by-Step Guide to Application
- Shake the bottle to mix the solution thoroughly.
- Warm the drops in your hand for a minute to avoid dizziness from cold liquid.
- Lie down with the affected ear upward, instill 2–3 drops, and stay in position for about a minute.
- Keep the dropper tip clean by avoiding contact with the ear or other surfaces.
Recommended Dosage
Most prescriptions call for 2–3 drops, 2–3 times daily, for 7–10 days. Overusing the drops can thin the ear canal skin, increasing infection risk. If symptoms don’t improve, consult your doctor rather than extending use. Dosage adjustments should only be made under medical supervision.
Storage Tips
Store betamethasone at room temperature (15–25°C), away from direct sunlight or moisture. Keep the bottle tightly closed when not in use. Proper storage ensures the medication remains effective throughout the treatment course. Check the expiration date before use and discard if outdated.
Side Effects to Watch For
While betamethasone is generally safe, it can cause side effects in some users. Knowing what to expect helps you monitor for issues and seek help if needed. Most side effects are mild, but serious risks require immediate attention.
Common Side Effects
Some users experience mild burning or stinging after applying the drops, which usually fades quickly. Temporary itching or irritation in the ear canal is also possible. These effects rarely require intervention unless they persist or intensify over time.
Rare but Serious Risks
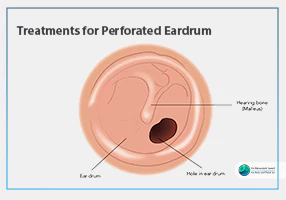
In rare cases, allergic reactions like rash or swelling may occur. Prolonged use can thin the ear canal skin, making it more prone to infections. If used with a perforated eardrum, betamethasone may enter the middle ear, potentially causing hearing loss or infection. Seek medical advice if you notice unusual symptoms.
Precautions for Safe Use
 Certain conditions and situations require extra caution when using betamethasone. Misuse can worsen symptoms or lead to complications, so understanding these precautions is essential.
Certain conditions and situations require extra caution when using betamethasone. Misuse can worsen symptoms or lead to complications, so understanding these precautions is essential.
Who Should Avoid Betamethasone
Betamethasone is not suitable for viral or fungal ear infections, as corticosteroids can aggravate these conditions. It’s also contraindicated with a perforated eardrum unless approved by a specialist. Always inform your doctor of any allergies or medical history before starting treatment.
Use in Special Populations
Children, pregnant women, or breastfeeding mothers should use betamethasone only under strict medical supervision. The drops may be safe in these groups, but potential risks require careful monitoring. Regular ENT checkups ensure safe and effective use.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
If tinnitus or ear discomfort persists after a week, or if new symptoms like discharge or hearing loss appear, contact your doctor. Regular follow-ups help assess treatment progress and adjust the plan if needed. Don’t ignore worsening symptoms, as they may indicate a serious issue.
Complementary Strategies for Tinnitus Relief
 Betamethasone can be part of a broader tinnitus management plan. Combining medical treatment with lifestyle changes can enhance relief and improve quality of life. Explore these strategies to support your treatment.
Betamethasone can be part of a broader tinnitus management plan. Combining medical treatment with lifestyle changes can enhance relief and improve quality of life. Explore these strategies to support your treatment.
Sound Therapy Options
White noise machines, hearing aids, or smartphone apps can mask tinnitus sounds, making them less intrusive. These tools are especially helpful at night when tinnitus can disrupt sleep. Consult an audiologist to find the best sound therapy for your needs.
Lifestyle and Stress Management
Stress often worsens tinnitus perception, so techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help. Avoiding triggers like caffeine, nicotine, or loud noises also reduces symptom severity. A healthy diet and regular exercise support overall ear health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Betamethasone doesn’t cure tinnitus but can reduce symptoms linked to inflammation. An ENT specialist can recommend other treatments for non-inflammatory causes.
Relief may start within a few days, but full effects depend on the condition’s severity. If no improvement occurs after a week, consult your doctor.
No, prolonged use can cause skin thinning or infections. Follow the prescribed duration, typically 7–10 days, and seek medical advice for extended needs.
Stop using the drops and see a specialist immediately, as betamethasone can cause complications with a perforated eardrum.
Related Articles
Online Consultation, Directly with Dr. Saeedi
Ask your question via WhatsApp, and if you wish, Send your photo for a more accurate assessment.
Free Consultation on WhatsApp